Motivation
The forthcoming release will include smart assets and trading for smart accounts. This post is intended to highlight the distinctions that smart assets have.
Asset supported transactions
The following transaction types are validated by smart assets’ scripts:
- TransferTransaction
- ReissueTransaction
- BurnTransaction
- ExchangeTransaction
- MassTransferTransaction
- SetAssetScriptTransaction
The following transaction types are not validated by smart assets’ scripts:
- IssueTransaction
An asset that is already issued cannot be issued again, so validating IssueTransactions by smart asset’s script doesn’t make sense.
- SetSponsorshipTransaction
Sponsorship of smart assets was prohibited due to the fact that sponsorship actually allows you to transfer an asset to its issuer without executing the script, so it causes transfer of assets that is not validated by the script. Alternatively, if the script will validate this, it is not clear exactly how and with what branch. However, when an asset issuer sets sponsorship to the asset, they may foresee this situation. Therefore, smart asset sponsorship can be allowed, if necessary.
- LeaseTransaction, LeaseCancelTransaction, AliasTransaction, DataTransaction, SetScriptTransaction
These transactions don’t involve any assets.
Access to proofs from scripts
Access to proofs from smart assets’ scripts is denied in order to guarantee no collisions with processing proofs in smart accounts’ scripts.
For example, if a smart asset’s script requires that all the transactions with this asset had a certain value written in proofs[1], then smart accounts that use multi-signature and refer to proofs[1], are not able use this asset.
Validation in smart trading
Smart accounts’ scripts validate both Orders and ExchangeTransactions. Smart assets’ scripts validate only ExchangeTransactions.
For example, you want to validate Orders that are placed by your account. You shouldn’t be able to filter counter-orders, because they are placed by someone else. Because of that an “order” branch has been made - in this branch you have access to your Order fields only.
You can also validate your ExchangeTransactions with your account’s script but in that case, the validation will have a different meaning: you will take on the role of a scripted matcher. In this case, you have access to all fields of the transaction, including the orders.
The smart assets’ scripts validate ExchangeTransactions but not Orders. There is no need to restrict access to a counter-order because the order does not belong to an asset. Moreover, the asset is present in both orders (asset pairs in both orders are the same), and there is no need to validate each of these orders separately with an asset script.
Fee Calculation Rules for Trading
If an asset pair contains a smart asset then the fee is increased by + 0.004 (+0.008 if both assets are smart). It doesn’t matter if any of the accounts is a smart account, smart accounts pay in the same way as non-smart accounts do.
| Asset Pair | Fee |
|---|---|
| Asset / Asset | 0.003 |
| Asset / Smart asset | 0.003 + 0.004 = 0.007 |
| Smart asset / Smart asset | 0.003 + 0.008 = 0.011 |
This fee is paid to the matcher by every account that is placing an order. The same fee is paid by the matcher when an ExchangeTransaction is put into the blockchain.
If an ExchangeTransaction’s sender (the matcher or any other account) has a script then the total fee for the transaction is increased by 0.004 waves.
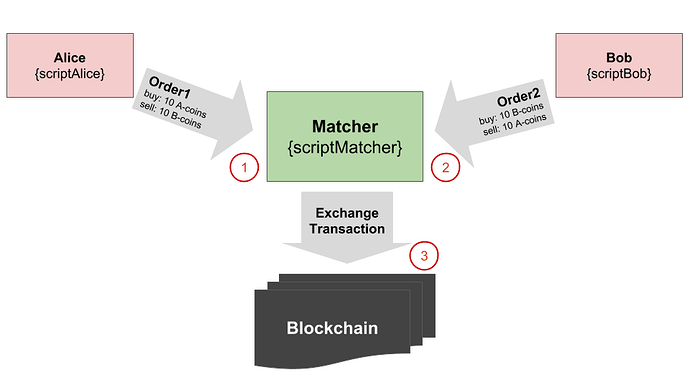
Example
Let’s consider an exchange of two smart assets:
Alice and Bob (both have smart accounts) place their orders to the matcher (the matcher has its own script). When the two orders have matched, the matcher creates an ExchangeTransaction and tries to put it into the blockchain.
In this case, the following validations are performed:
- Matcher validates Order1
- with scriptAlice (case Order => )
- with assetScriptA (case ExchangeTransaction => )*
- with assetScriptB (case ExchangeTransaction => )*
- Matcher validates Order2
- with scriptBob (case Order => )
- with assetScriptA (case ExchangeTransaction => )*
- with assetScriptB (case ExchangeTransaction => )*
- Node validates ExchangeTransaction
- with scriptMatcher (case ExchangeTransaction => )
- with assetScriptA (case ExchangeTransaction => )
- with assetScriptB (case ExchangeTransaction => )
- validates ExchangeTransaction.buyOrder with scriptAlice (case Order => )
- validates ExchangeTransaction.sellOrder with scriptBob (case Order => )
*Matcher validates Orders by the assets’ scripts as follows: the matcher creates an auxiliary counter-order, puts the two orders to an ExchangeTransaction and validates this transaction via the assets scripts’ “case tx: ExchangeTx => …” branches.
As a result, for the Orders placement Alice pays fee=0.011 waves to the matcher, Bob pays fee=0.011 waves to the matcher. When the ExchangeTransaction is being put into the blockchain, the fee payed by the matcher is 0.011+0.004(because of the matcher’s script)=0.015 waves.